The tussle between TOR and the FBI dates way back to this privacy suite’s initial days. TOR might be a solid pal in
keeping your online life private, but the FBI has managed to breach
this security layer from time-to-time. The FBI is known to be involved
in a fair share of efforts made to uncover TOR’s privacy layers.
Such
developments have been made public in recent time, thanks to numerous
court cases that tell us about FBI’s hacking tools like Network Investigative Technique (NIT). Another similar set of allegations were made by the TOR Director who accused the FBI of spending $1 Million on TOR-hacking research being carried out at the Carnegie Mellon University.According to a new paper, TOR is working closely with security researchers to develop a new version of the TOR browser. This new and “hardened” version of TOR will come with new techniques to defeat hacking attempts by the FBI and other government agencies.
Called “Selfrando“, the researchers are using a technique to avert the web browser exploits being used by the FBI. This new method will fight the FBI’s “Code Reuse” exploits. It’s a way to utilize the memory leak and make use of code libraries that are already present in the browser.
In simpler words, Code Reuse develops malware inside a software’s memory by rearranging stuff and avoids the tougher task of injecting new notorious code.
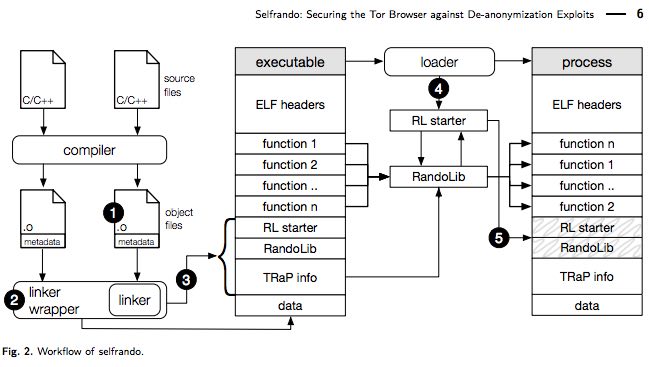
To fight this technique, Selfrando creates a random address space for application’s codes and makes the exploit tougher. This technique aims to replace Firefox’s standard address space layout randomization (ASLR) techniques.
This means that after this development and a new version of Selfrando-equipped TOR, it would be difficult for the law enforcement agencies to hack into a TOR-enabled system.
It’s pleasing to see that the researcher community is partnering with the TOR Project to make our web a safer place.